Title: Optimizing urban three-dimensional landscapes in potential development areas to mitigate urban heat island effect under shared socioeconomic pathways
Abstract
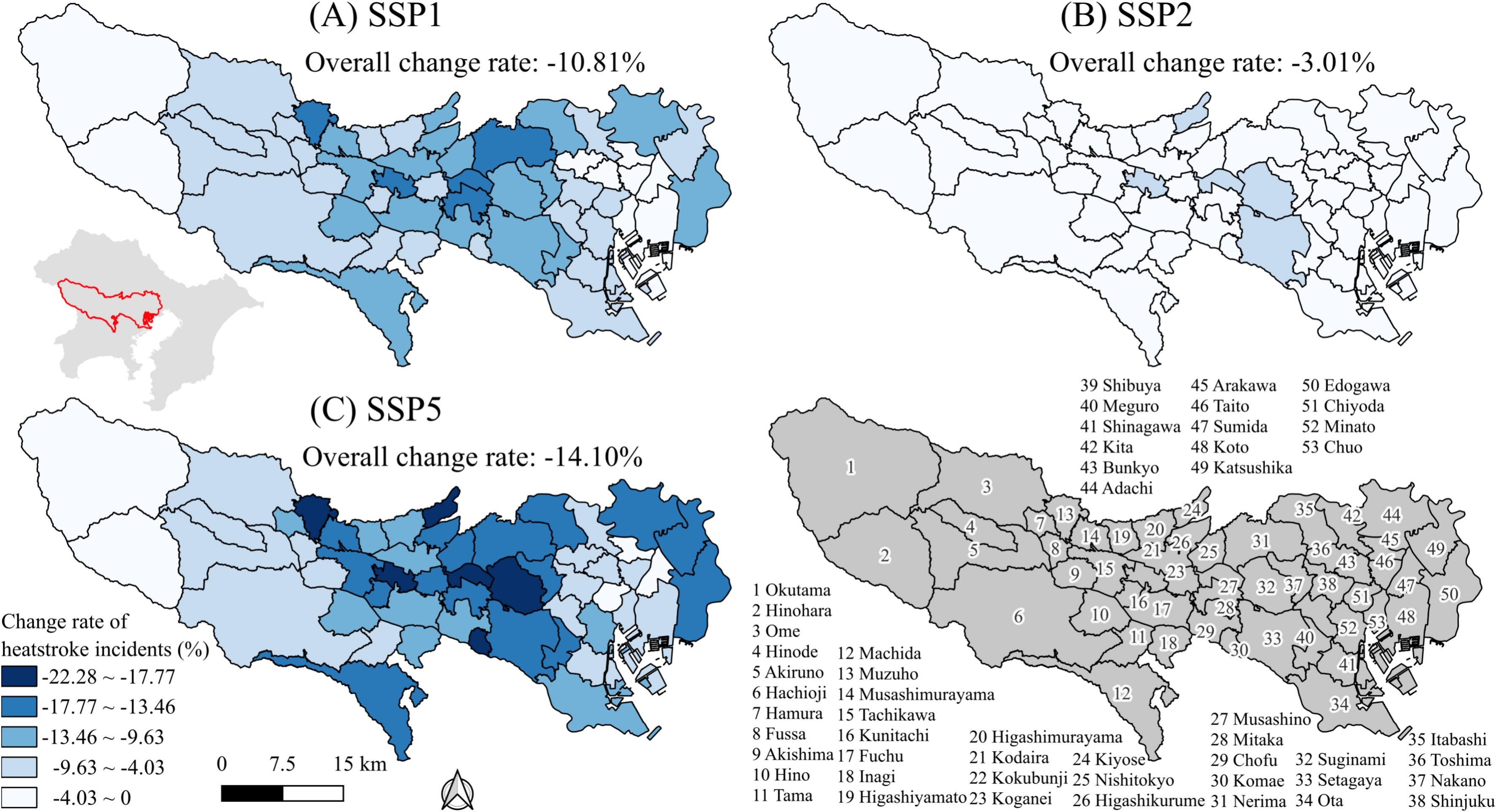
The urban heat island (UHI) effect threatens human health. While optimizing the spatial structure of urban land use presents a promising strategy for UHI mitigation, few studies examined the feasibility of urban three-dimensional landscape optimization in potential development areas (PDA), resulting in unsuitable optimization results and computational inefficiency. To address these limitations, we develop a novel multi-objective optimization model for urban three-dimensional landscapes in PDA (3DLS-PO) that integrates the patch-generating simulation (PLUS) model and the particle swarm optimization (PSO) algorithm. The PLUS model first simulates the PDA in the future under different scenarios. The PSO algorithm then allocates urban land use in the PDA to mitigate the UHI effects with the explored nonlinear relationship between land surface temperature (LST) and urban two- and three-dimensional landscapes. We applied the 3DLS-PO model to the Tokyo Metropolitan Area (TMA) for 2030 under the shared socioeconomic pathway (SSP) scenarios. The SSP5 scenario achieves the maximum LST reduction of 5.18%, followed by SSP1 (4.60%) and SSP2 (2.34%). To mitigate the UHI effects in the TMA, high-rise buildings should be placed at the periphery of the TMA, low-rise buildings should be allocated to the suburbs, and green spaces should be scattered. The optimization results demonstrate substantial public health benefits, potentially preventing 3.01%-14.10% of heatstroke incidents in Tokyo. Incorporating the PDA also enhances the computational efficiency of the optimization process by 14 times. The 3DLS-PO model can provide support for addressing urban climate change.
Highlights
- Urban three-dimensional landscapes were incorporated during the optimization process.
- Performance of optimization was enhanced due to potential development areas.
- Future land use spatial structure was optimized under shared socioeconomic pathways.
- Decline in heatstroke incidents was projected based on the optimization results.
Keywords
Land use spatial structure optimization;
Urban heat island;
Urban three-dimensional landscape;
Potential development areas;
Shared socioeconomic pathways
Full Text Download
Q.E.D.









