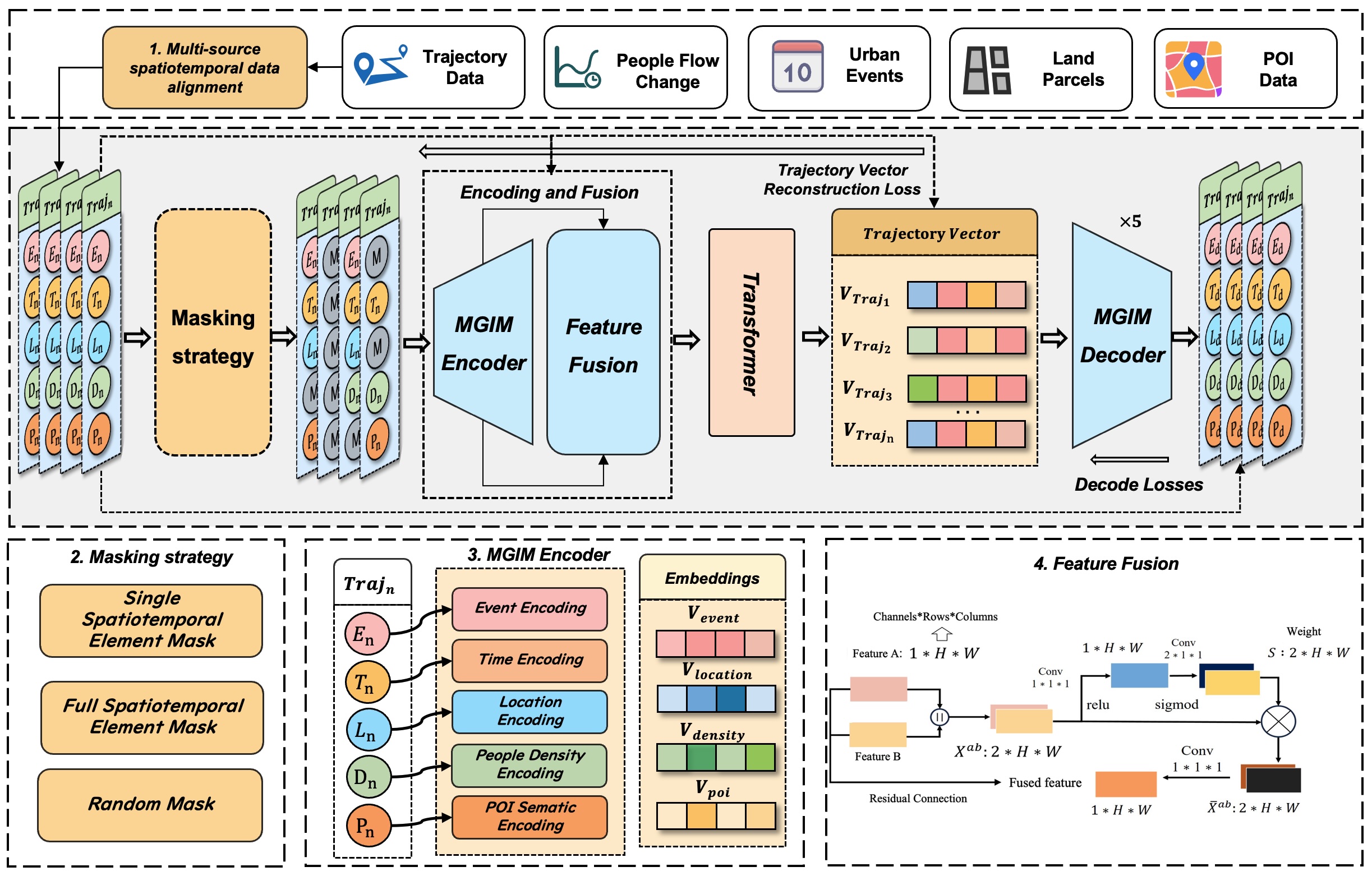
MGIM: Masked Geo-Inference for Land Parcels
Effective modeling of spatio-temporal contexts to support geographic reasoning is essential for advancing Geospatial Artificial Intelligence. Inspired by masked language models, this paper introduces the Masked Geographical Information Model (MGIM), a novel self-supervised framework for learning context-aware representations from multi-source spatio-temporal data. The framework’s core innovations include a parcel-scale method for multi-source data fusion and a custom self-supervised masking strategy for diverse geographic elements. This integrated modeling approach enables the model to capture complex spatio-temporal relationships and achieve consistently strong performance across diverse geographic reasoning tasks, such as trajectory inference, people flow inference, event identification, and land parcel function analysis. MGIM accurately reasons from spatio-temporal contexts and dynamically adjusts inferences according to contextual changes. The visualization of attention mechanisms further illustrates MGIM’s capacity to construct contextually-aware representations and task-specific attention patterns analogous to natural language processing models. This study presents a new paradigm for general-purpose spatio-temporal modeling in real-world geographic scenarios, offering significant theoretical and practical value, and promising an effective solution for building a geographic foundation model.
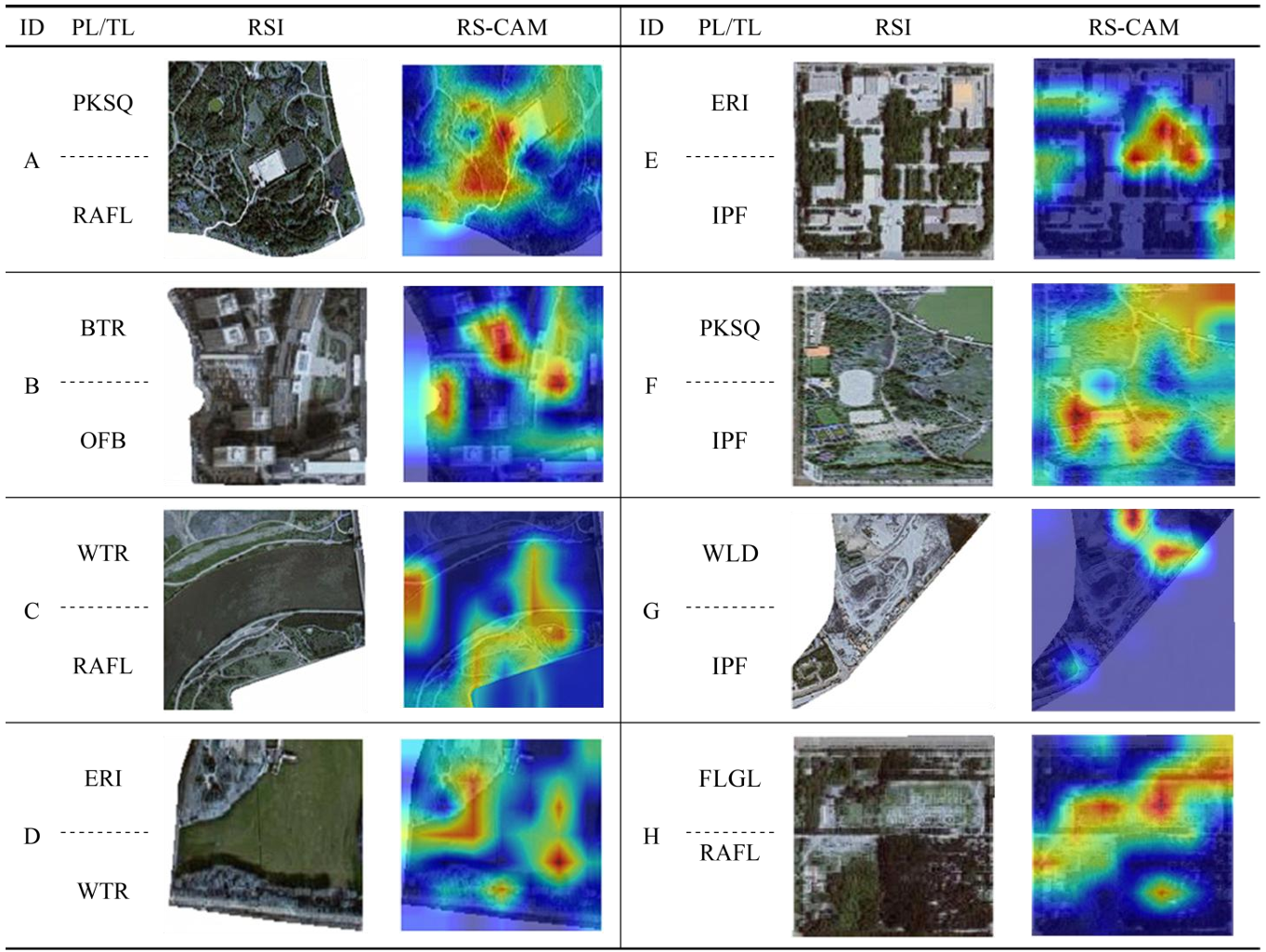
TIA-Net: Multi-Modal Land Use Recognition
With the increasing demand for refined urban management, methods that rely on a single data source or coarse-grained land use classification are no longer sufficient. Therefore, this paper proposes a parcel-level fine-grained land use recognition model, called the Triple Interaction Attention Network (TIA-Net). TIA-Net integrates remote sensing imagery (RSI), semantic information of points of interest (POI), and temporal population density (TPD). Swin-BiFPN is used to extract multi-scale spatial features from RSI. HydraMultiRocketPlus is used to model the temporal dynamics of population mobility. The POI encoder is used to characterize the distribution of human activities. Based on these components, the Feature-preserving Triple Interaction Self-Attention (FP-TISA) module is proposed. FP-TISA achieves deep fusion across spatial, semantic, and temporal dimensions. The module can effectively capture nonlinear interactions between heterogeneous data. The module can also reduce feature loss, which is common in traditional methods. On the national land use dataset CN-MSLU-100K, TIA-Net achieves a test accuracy of 77.64%, a Kappa coefficient of 0.740, and a macro-average precision of 65.20%, all outperforming the existing baseline models. Especially for macro-average accuracy, TIA-Net achieves nearly double the performance of the baseline model. Further analysis based on Grad-CAM++ and attention visualization reveals the model’s focus on key areas and its cross-modal interaction mechanism. In summary, TIA-Net improves both land use classification accuracy and interpretability. The model provides strong technical support for territorial spatial planning and natural resource management.
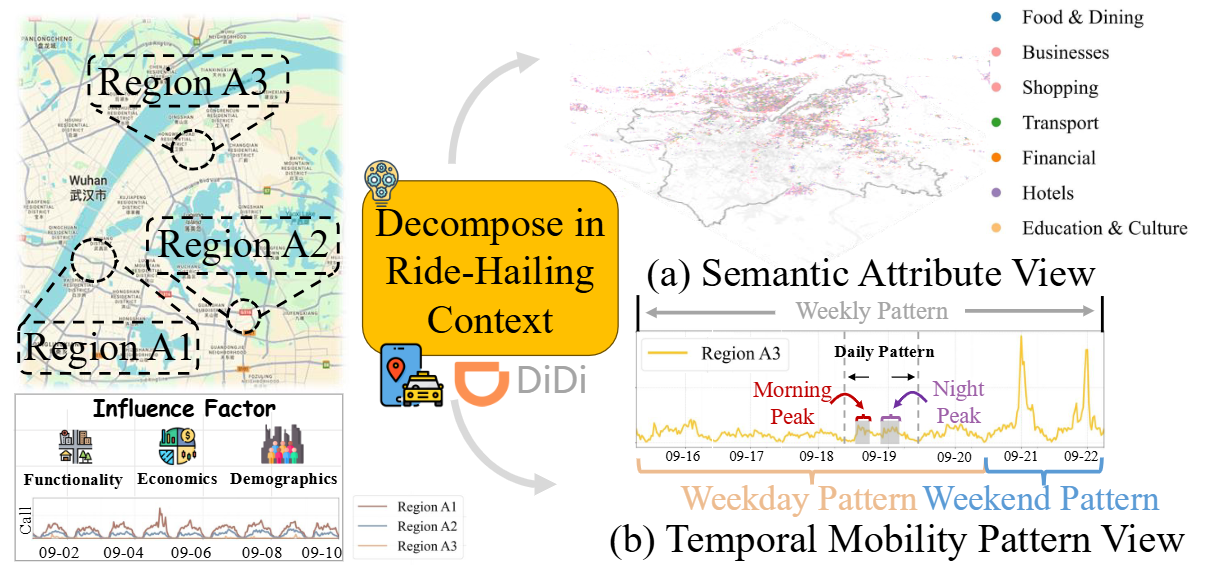
Multi-View Geospatial Learning for Ride-Hailing Forecasting at DiDi
The proliferation of ride-hailing services has fundamentally transformed urban mobility patterns, making accurate ride-hailing forecasting crucial for optimizing passenger experience and urban transportation efficiency. However, ride-hailing forecasting faces significant challenges due to geospatial heterogeneity and high susceptibility to external events. This paper proposes MVGR-Net (Multi-View Geospatial Representation Learning), a novel framework that addresses these challenges through a two-stage approach. In the pre-training stage, we learn comprehensive geospatial representations by integrating Points-of-Interest and temporal mobility patterns to capture regional characteristics from both semantic attribute and temporal mobility pattern views. The forecasting stage leverages these representations through a prompt-empowered framework that fine-tunes Large Language Models while incorporating external events. Extensive experiments on DiDi’s real-world datasets demonstrate the state-of-the-art performance.