Title: Nonlinear associations between street-level greenery quantity and quality, physical activity, and sedentary behaviour in Chinese middle-aged and older adults: A socioeconomic equity perspective
Abstract
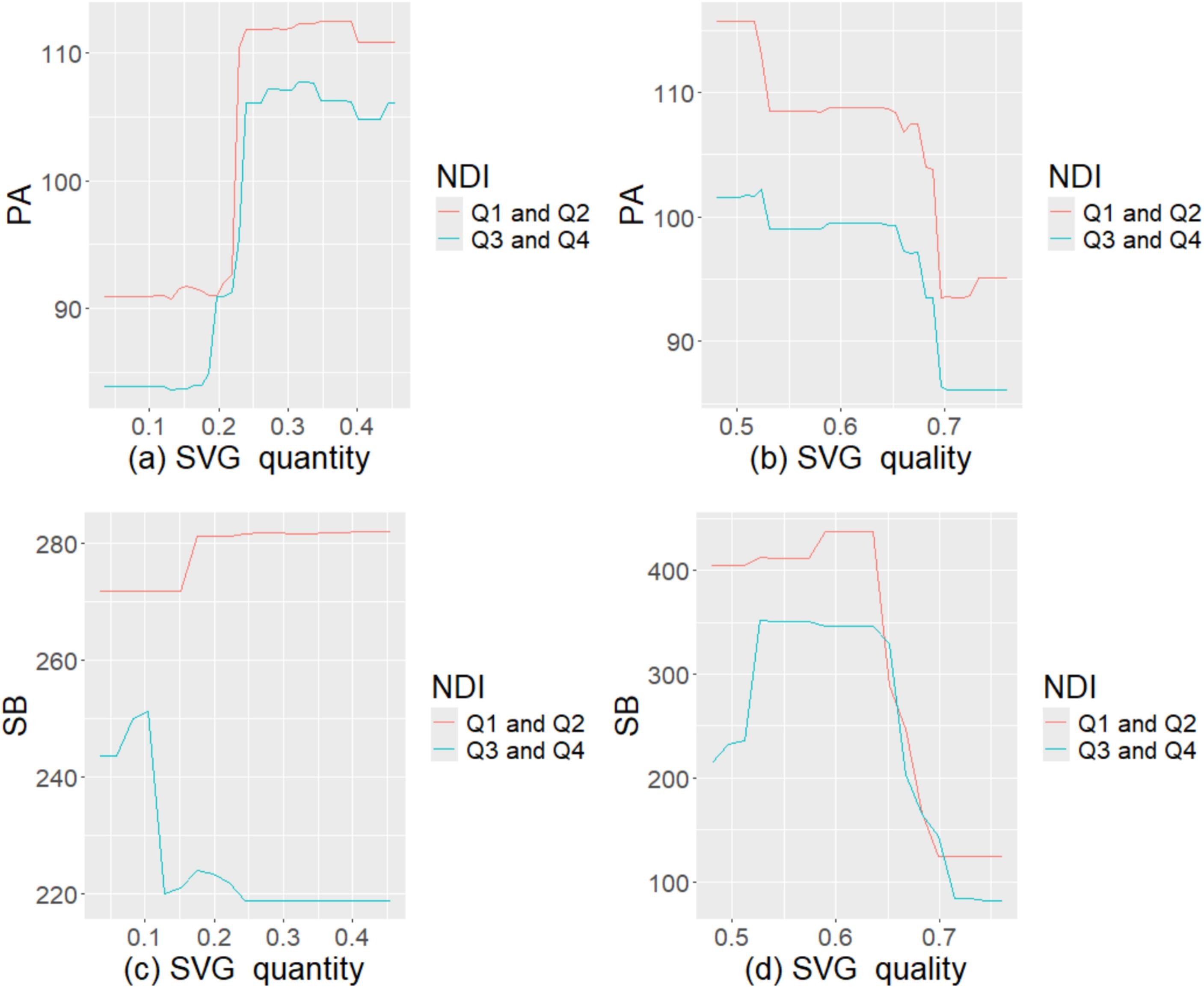
Despite studies investigating the relationships among greenery, physical activity, and sedentary behaviour, it remains unclear whether such associations are nonlinear. Scant attention has also been paid to the role of greenery from a socioeconomic equity perspective. Thus, we assessed possible nonlinear associations between street-level greenery, physical activity, and sedentary behaviour in middle-aged and older adults. We also examined whether and how street-level greenery may increase socioeconomic equity in physical activity and sedentary behaviour. Data on physical activity and sedentary behaviour were obtained from the WHO Study on Global Ageing and Adult Health in Shanghai, China. The quantity and quality of street-level greenery were assessed using segmented street-view images based on deep learning methods. The results of fitting gradient-boosting decision trees showed that street-level greenery quantity was positively related to physical activity. We observed a steep increase in physical activity at low greenery quantity and flattening out at higher quantity. Street-level greenery quality was negatively related to sedentary behaviour. While sedentary behaviour did not change significantly at low greenery quality, the decrease became steep at higher quality. The greenery association was stronger for low incomers and those in deprived neighbourhoods.
Keywords
Middle-aged and older;
Nonlinear effects;
Street-level greenery;
Physical activity and sedentary behaviour;
Socioeconomic equity
Full Text Download
Q.E.D.









